Soldiers Were First: How and why the states started and now handle early and absentee voting explores the fascinating history of voting rights for military personnel and how it shaped the landscape of early and absentee voting for all citizens.
This journey through time reveals how the unique challenges faced by soldiers during wartime led to the development of innovative voting methods, paving the way for the modern-day practices we see today.
From the early days of the Republic, soldiers have played a vital role in shaping the nation’s democracy. Their right to vote, even while deployed in distant lands, underscores the fundamental belief in the importance of civic participation. This exploration delves into the historical context of soldiers’ voting rights, tracing the evolution of laws and procedures, and examining the impact of technological advancements on the accessibility and ease of absentee voting.
Future Trends: Soldiers Were First: How And Why The States Started And Now Handle Early And Absentee Voting
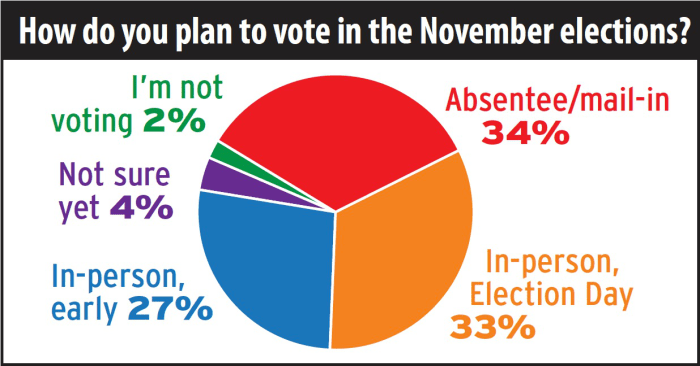
The landscape of early and absentee voting is poised for significant evolution, driven by technological advancements, shifting demographics, and evolving voter preferences. These forces are shaping a future where voting becomes more accessible, convenient, and inclusive for all Americans.
You also can understand valuable knowledge by exploring ‘Chaos is the point’: MAGA-dominated Georgia election board makes IMPOSSIBLE new rule favoring Trump.
The Role of Technology in Expanding Voting Access, Soldiers were first: How and why the states started and now handle early and absentee voting
Technology is playing a pivotal role in making voting more accessible and convenient. Online voting platforms and mobile voting apps are emerging as powerful tools to simplify the voting process.
- Online Voting Platforms:These platforms allow voters to register, request ballots, and cast votes securely from their computers or mobile devices. Examples include the “Vote by Mail” system used in Oregon, which allows voters to register and vote entirely online.
- Mobile Voting Apps:Mobile apps offer a user-friendly interface for voters to access election information, track their ballot status, and even cast votes on their smartphones. The “Vote.gov” app, developed by the U.S. Election Assistance Commission, provides voters with information about elections, polling places, and candidate information.
Closing Summary

The evolution of early and absentee voting is a testament to the ongoing struggle for greater access to the ballot box for all citizens. As technology continues to advance and demographics shift, the future of voting promises further innovation and adaptation.
By understanding the historical context and the challenges faced in ensuring secure and accessible voting, we can work towards a future where every eligible citizen has the opportunity to participate in our democracy, regardless of location or circumstance.
Questions and Answers
How do states differ in their early and absentee voting laws?
States have varying eligibility criteria, deadlines, application methods, and voting options for early and absentee voting. Some states offer more flexibility than others, with different types of absentee ballots available, including mail-in ballots, in-person voting at designated locations, and even online voting options in some cases.
What are some common concerns about early and absentee voting?
Concerns include voter fraud, the potential for manipulation, and ensuring the integrity of the electoral process. However, many states have implemented safeguards and verification procedures to address these concerns, such as voter ID requirements, signature verification, and secure ballot handling practices.
What are some potential future trends in early and absentee voting?
Future trends may include increased use of online voting platforms, mobile voting apps, and other technological advancements that make voting more accessible and convenient. Additionally, the growing diversity of the electorate may lead to greater focus on accessibility for individuals with disabilities and language barriers.
 CentralPoint Latest News
CentralPoint Latest News
