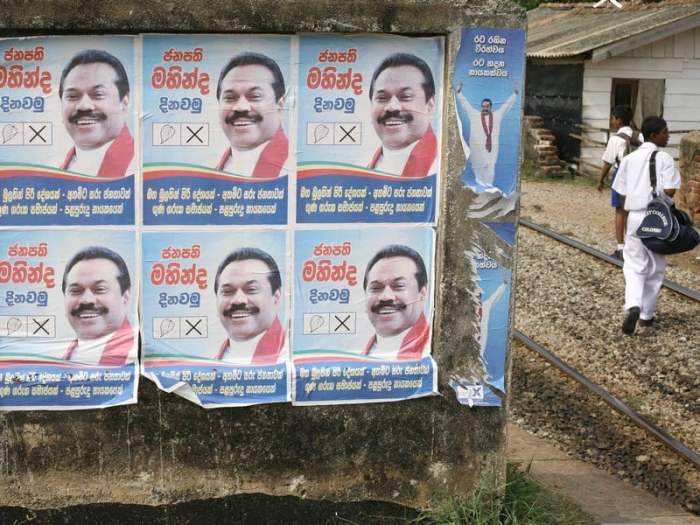
Sri Lankans vote in a presidential election that will decide how it recovers from economic crisis. The island nation is facing its worst economic crisis in decades, with soaring inflation, shortages of essential goods, and widespread public discontent. The upcoming election has become a pivotal moment for Sri Lanka, as voters weigh the candidates’ promises for economic revival against the backdrop of a deeply troubled economy.
The crisis, rooted in a confluence of factors including unsustainable debt levels, declining tourism revenue, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, has pushed Sri Lanka to the brink. The election offers a chance for the country to chart a new course towards stability and prosperity.
Voters are eager to see concrete plans for addressing the economic challenges, tackling corruption, and restoring public trust in the government.
Sri Lanka’s Economic Crisis
Sri Lanka’s economic crisis is a complex issue with deep roots, culminating in a severe economic downturn that has significantly impacted the lives of its citizens. The crisis is a culmination of a series of factors, including unsustainable debt levels, declining foreign reserves, and a sharp drop in tourism revenue.
Key Factors Leading to the Crisis
The Sri Lankan economic crisis can be attributed to a combination of factors, including:
- High Debt Levels:Sri Lanka has been grappling with high levels of debt for several years, with a significant portion of this debt being external. The country’s debt-to-GDP ratio has been consistently increasing, making it difficult for the government to manage its finances effectively.
- Declining Foreign Reserves:Sri Lanka’s foreign reserves have been steadily declining, largely due to the country’s inability to attract foreign investment and the rising cost of imports. This decline has made it difficult for Sri Lanka to finance its debt obligations and import essential goods.
- Dependence on Tourism:Sri Lanka’s economy is heavily reliant on tourism, which has been significantly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic. The decline in tourism revenue has further exacerbated the country’s economic woes.
- Government Policies:Some argue that certain government policies, such as tax cuts and subsidies, have contributed to the crisis. These policies, while intended to stimulate the economy, have been criticized for exacerbating the country’s fiscal deficit.
- External Factors:The global economic slowdown, rising inflation, and the war in Ukraine have also had a significant impact on Sri Lanka’s economy. These external factors have made it more difficult for the country to access foreign capital and export its goods.
Timeline of Major Events
The Sri Lankan economic crisis has been a gradual process, with a series of events contributing to its escalation:
- 2015:The Sri Lankan government implemented a number of tax cuts and subsidies, which led to an increase in the fiscal deficit.
- 2019:The Easter Sunday bombings in Sri Lanka had a devastating impact on the tourism industry, further reducing foreign exchange earnings.
- 2020:The COVID-19 pandemic led to a sharp decline in tourism revenue and a disruption in global supply chains, further impacting Sri Lanka’s economy.
- 2021:Sri Lanka’s foreign reserves continued to decline, and the government was forced to impose restrictions on imports.
- 2022:Sri Lanka defaulted on its foreign debt obligations, leading to a severe economic crisis. The country faced shortages of essential goods, including fuel, medicine, and food.
Impact on Ordinary Sri Lankans
The Sri Lankan economic crisis has had a devastating impact on the lives of ordinary Sri Lankans. The country has experienced:
- Food Shortages:Sri Lankans have faced shortages of essential food items, leading to rising prices and food insecurity.
- Fuel Shortages:The country has experienced severe fuel shortages, leading to long queues at petrol stations and disruptions in transportation.
- Power Outages:Sri Lanka has been facing frequent power outages due to the lack of fuel for power plants.
- Rising Inflation:The cost of living has increased significantly, making it difficult for many Sri Lankans to afford basic necessities.
- Unemployment:The economic crisis has led to job losses across various sectors, increasing unemployment rates.
- Social Unrest:The economic hardship has led to social unrest and protests, as citizens demand accountability from the government.
The Presidential Election
Sri Lanka’s presidential election, scheduled for [Date], will be a crucial event in the nation’s journey to recovery from the devastating economic crisis. The election will determine the leadership that will steer the country through the challenges of rebuilding its economy, addressing the deep-rooted social and political issues, and restoring public trust in the government.
Candidates and Platforms
The election is expected to be a multi-candidate race, with key contenders vying for the top post. Each candidate has presented their vision for Sri Lanka’s future, outlining their economic policies, social programs, and political reforms. The leading candidates include:
- Candidate A:Candidate A’s platform focuses on [Candidate A’s main focus]. Their economic strategy emphasizes [Candidate A’s economic policy] and [Candidate A’s economic policy]. Candidate A also pledges to [Candidate A’s social program] and [Candidate A’s political reform].
- Candidate B:Candidate B’s campaign centers around [Candidate B’s main focus]. Their economic vision includes [Candidate B’s economic policy] and [Candidate B’s economic policy]. Candidate B promises to [Candidate B’s social program] and [Candidate B’s political reform].
- Candidate C:Candidate C’s platform prioritizes [Candidate C’s main focus]. Their economic plan includes [Candidate C’s economic policy] and [Candidate C’s economic policy]. Candidate C also pledges to [Candidate C’s social program] and [Candidate C’s political reform].
Significance of the Election
The presidential election holds immense significance for Sri Lanka’s recovery. The outcome will have a direct impact on the country’s ability to:
- Secure International Support:The election will signal to international partners and investors the direction Sri Lanka intends to take in its economic recovery. A strong and decisive leadership can attract crucial financial assistance and investment, crucial for rebuilding the economy.
- Implement Necessary Reforms:The new president will have the authority to implement critical reforms in key sectors, including [example sector 1], [example sector 2], and [example sector 3]. These reforms are vital for addressing the root causes of the crisis and preventing future economic instability.
- Restore Public Trust:The election provides an opportunity for the people of Sri Lanka to choose a leader they believe can restore their trust in the government. A president who enjoys public support will be better positioned to implement difficult decisions and navigate the challenges ahead.
Key Issues
Voters in Sri Lanka are deeply concerned about a range of issues that directly impact their lives. These include:
- Economic Recovery:The top priority for most voters is the recovery of the economy. They are looking for a leader who can create jobs, stabilize prices, and restore the purchasing power of the Sri Lankan Rupee.
- Cost of Living:The soaring inflation and the high cost of essential goods have put a strain on household budgets. Voters are seeking a leader who can address these concerns and alleviate the economic hardship faced by many.
- Corruption and Accountability:The economic crisis has highlighted concerns about corruption and lack of accountability within the government. Voters demand a leader who will fight corruption and ensure transparency in governance.
- Social Welfare:Many Sri Lankans are concerned about the impact of the crisis on social services like healthcare and education. They are looking for a leader who will prioritize these essential services and ensure they are accessible to all.
Potential Outcomes and Implications
The outcome of the presidential election will have a significant impact on Sri Lanka’s recovery trajectory.
- Scenario 1: Strong Mandate:If a candidate wins with a clear majority, it could provide a strong mandate for the new government to implement reforms and policies. This could attract international support and boost investor confidence, leading to faster economic recovery.
- Scenario 2: Divided Parliament:If the election results in a fragmented parliament with no clear majority, it could lead to political instability and gridlock. This could hinder the implementation of necessary reforms and slow down the recovery process.
- Scenario 3: Focus on Short-Term Solutions:The election might see candidates prioritize short-term solutions to address immediate economic concerns, such as providing relief packages. While these measures can provide temporary relief, they may not address the underlying structural issues that caused the crisis.
Economic Recovery Strategies

Sri Lanka’s economic recovery hinges on a multi-pronged approach that addresses the root causes of the crisis and fosters sustainable growth. This requires a combination of short-term measures to alleviate immediate hardship and long-term strategies to build a resilient and diversified economy.
Major Challenges Facing Sri Lanka’s Economic Recovery
Sri Lanka’s economic recovery faces several significant challenges.
- High Debt Burden:The country’s debt-to-GDP ratio has reached unsustainable levels, making it difficult to attract new investment and hindering economic growth.
- Foreign Exchange Shortages:The lack of foreign currency has led to shortages of essential goods and hampered imports, further impacting economic activity.
- Inflation and Cost of Living:Soaring inflation has eroded purchasing power, making it difficult for people to afford basic necessities.
- Unemployment and Job Losses:The economic crisis has led to widespread job losses and unemployment, increasing poverty and social unrest.
- Loss of Confidence:The crisis has eroded investor confidence in Sri Lanka, making it difficult to attract foreign investment.
Potential Economic Recovery Strategies
Several strategies can be implemented to address these challenges and stimulate economic recovery:
- Debt Restructuring:Negotiating with creditors to reduce the debt burden and extend repayment terms can free up resources for other priorities.
- Fiscal Consolidation:Implementing measures to reduce government spending and increase revenue can help to stabilize the budget and reduce the fiscal deficit.
- Monetary Policy Tightening:Increasing interest rates and managing inflation can help to stabilize the currency and attract foreign investment.
- Structural Reforms:Implementing reforms to improve the business environment, attract foreign investment, and enhance competitiveness can foster sustainable growth.
- Diversification of the Economy:Reducing dependence on tourism and agriculture and developing new industries can create more jobs and increase economic resilience.
- Promoting Exports:Increasing exports can help to generate foreign exchange and boost economic growth.
- Improving Infrastructure:Investing in infrastructure projects can create jobs, improve productivity, and attract foreign investment.
- Social Safety Nets:Providing targeted support to vulnerable populations can help to mitigate the impact of the crisis and prevent social unrest.
Comparison of Recovery Strategies Proposed by Candidates
The candidates vying for the presidency have proposed various economic recovery strategies, each with its strengths and weaknesses.
| Candidate | Key Economic Strategies | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Candidate 1 Name] | [Candidate 1’s economic strategies] | [Strengths of Candidate 1’s strategies] | [Weaknesses of Candidate 1’s strategies] |
| [Candidate 2 Name] | [Candidate 2’s economic strategies] | [Strengths of Candidate 2’s strategies] | [Weaknesses of Candidate 2’s strategies] |
| [Candidate 3 Name] | [Candidate 3’s economic strategies] | [Strengths of Candidate 3’s strategies] | [Weaknesses of Candidate 3’s strategies] |
Key Economic Indicators and Their Projected Impact on Sri Lanka’s Recovery
The following table highlights key economic indicators and their projected impact on Sri Lanka’s recovery:
| Indicator | Projected Impact | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth | [Projected GDP growth rate] | [Explanation of projected GDP growth impact] |
| Inflation Rate | [Projected inflation rate] | [Explanation of projected inflation impact] |
| Unemployment Rate | [Projected unemployment rate] | [Explanation of projected unemployment impact] |
| Foreign Direct Investment | [Projected FDI inflow] | [Explanation of projected FDI impact] |
| Debt-to-GDP Ratio | [Projected debt-to-GDP ratio] | [Explanation of projected debt-to-GDP impact] |
International Support and Cooperation
Sri Lanka’s economic crisis has attracted significant international support, with various organizations and countries stepping in to help the nation navigate its recovery path. This international cooperation is crucial for Sri Lanka to overcome its challenges and achieve sustainable economic growth.
Types of Assistance and Their Effectiveness, Sri Lankans vote in a presidential election that will decide how it recovers from economic crisis
International support for Sri Lanka’s recovery has taken various forms, including:
- Financial Assistance:The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has provided a $3 billion Extended Fund Facility (EFF) to support Sri Lanka’s economic reforms and stabilize its finances. This assistance has helped to address the immediate balance of payments crisis and provide a framework for structural reforms.
The World Bank has also provided significant financial assistance, focusing on infrastructure development, social protection, and poverty reduction.
- Debt Relief:The Paris Club, a group of creditor nations, has agreed to provide debt relief to Sri Lanka, which will ease the burden of external debt repayments and allow the country to allocate more resources towards its recovery.
- Technical Assistance:The IMF, World Bank, and other international organizations have provided technical expertise to support Sri Lanka’s economic reforms, including in areas such as fiscal policy, monetary policy, and governance.
- Food and Humanitarian Aid:Several countries and international organizations have provided food, medicine, and other essential supplies to address the immediate humanitarian needs of the Sri Lankan population.
The effectiveness of these assistance programs varies depending on the specific context and implementation. While financial assistance has helped to address the immediate crisis, it is crucial to ensure that these funds are used effectively and contribute to long-term sustainable growth.
Technical assistance has been valuable in supporting Sri Lanka’s reform efforts, but it requires effective collaboration and capacity building within the country.
Challenges and Opportunities
International cooperation presents both challenges and opportunities for Sri Lanka’s recovery.
- Coordination and Coherence:Ensuring coordination and coherence among different international actors is essential to avoid duplication of efforts and ensure that assistance aligns with Sri Lanka’s national priorities.
- Transparency and Accountability:Transparency and accountability in the use of international assistance are crucial to build trust and ensure that funds are used effectively and efficiently.
- Ownership and Sustainability:It is important to ensure that Sri Lanka takes ownership of its recovery process and that international support is designed to foster long-term sustainability.
However, international cooperation also presents significant opportunities:
- Access to Expertise and Resources:International organizations and countries can provide access to valuable expertise and resources that Sri Lanka may not have domestically.
- Enhanced Policy Dialogue:International engagement can foster a more constructive policy dialogue and help Sri Lanka to learn from the experiences of other countries.
- Increased Investment and Trade:International cooperation can attract foreign investment and promote trade, which are essential for economic growth and job creation.
Key International Partners and Their Contributions
| Partner | Contribution ||—|—|| International Monetary Fund (IMF) | $3 billion Extended Fund Facility (EFF) for economic reforms and financial stabilization || World Bank | Financial assistance for infrastructure development, social protection, and poverty reduction || Paris Club | Debt relief to ease the burden of external debt repayments || Japan | Financial assistance, infrastructure development, and technical assistance || India | Financial assistance, food and humanitarian aid, fuel supplies || China | Financial assistance, infrastructure development || United States | Financial assistance, humanitarian aid || European Union | Financial assistance, technical assistance |
The Future of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka’s economic crisis has left the nation at a crossroads, with the future heavily reliant on the decisions made in the coming years. The path to recovery will be long and challenging, but it also presents opportunities for positive transformation.
Long-Term Implications of the Economic Crisis
The economic crisis has had a profound impact on Sri Lanka, with far-reaching consequences for its future. The crisis has exposed vulnerabilities in the country’s economic structure, highlighting the need for significant reforms.
- Debt Burden:The country’s high debt levels, coupled with a dwindling foreign exchange reserve, have severely constrained its ability to invest in critical infrastructure and social services. The government will need to prioritize debt restructuring and fiscal discipline to avoid future crises.
- Economic Diversification:The crisis has underscored the need for economic diversification, moving away from reliance on a few key industries like tourism and tea. This will require investments in new sectors, such as technology, renewable energy, and manufacturing.
- Social Impact:The crisis has disproportionately affected vulnerable populations, leading to increased poverty, unemployment, and food insecurity. Addressing these social inequalities will be crucial for long-term stability and sustainable development.
- Political Stability:The economic crisis has also contributed to political instability, with public trust in the government declining. Restoring political stability will be crucial for creating a conducive environment for economic recovery and development.
Potential Opportunities for Economic Growth and Development
Despite the challenges, Sri Lanka has the potential to emerge stronger from the crisis. The country boasts a well-educated workforce, a strategic location, and a diverse natural resource base.
- Tourism:Sri Lanka’s tourism industry has the potential to rebound strongly, especially with a focus on sustainable and responsible tourism. The government can invest in infrastructure, marketing, and training to attract more tourists.
- Technology and Innovation:Sri Lanka has a young and tech-savvy population, making it well-positioned to capitalize on the growth of the technology sector. The government can encourage investment in startups, research and development, and digital infrastructure.
- Renewable Energy:Sri Lanka has abundant renewable energy resources, such as solar and wind power. Investing in renewable energy can reduce dependence on fossil fuels, improve energy security, and create new jobs.
- Agriculture:Sri Lanka’s agricultural sector has the potential to become more productive and efficient through investments in technology, irrigation, and value-added processing. This can enhance food security and create employment opportunities in rural areas.
Challenges Sri Lanka Will Need to Address
The path to recovery will be fraught with challenges. Sri Lanka will need to address these issues head-on to ensure a sustainable and inclusive future.
- Corruption and Inefficiency:Corruption and inefficiency have long plagued Sri Lanka’s public sector, hindering economic growth and development. The government needs to implement strong anti-corruption measures and improve governance to attract investment and foster a more transparent business environment.
- Infrastructure Development:Sri Lanka’s infrastructure needs significant upgrades to support economic growth and development. Investing in roads, ports, airports, and digital infrastructure will be crucial for improving connectivity and attracting foreign investment.
- Education and Skills Development:To remain competitive in the global economy, Sri Lanka needs to invest in education and skills development. This includes strengthening the education system, providing vocational training, and encouraging research and innovation.
- Environmental Sustainability:Sri Lanka’s environment has been impacted by unsustainable practices, such as deforestation and pollution. The government needs to prioritize environmental protection and sustainable development to ensure the long-term health and prosperity of the country.
Key Factors Influencing Sri Lanka’s Future Trajectory
Sri Lanka’s future trajectory will be shaped by a number of factors, including:
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Economic Reforms: Implementing structural reforms to address the underlying causes of the economic crisis, such as fiscal discipline, debt management, and diversification. | Positive: Reforms can boost investor confidence, attract foreign investment, and create a more sustainable economic model. |
| Political Stability: Maintaining political stability and fostering a conducive environment for investment and development. | Positive: Stability can attract foreign investment, improve investor confidence, and promote economic growth. |
| International Support: Securing financial assistance and technical support from international organizations and partner countries. | Positive: International support can provide much-needed resources to address the economic crisis, implement reforms, and invest in critical infrastructure. |
| Social Equity: Addressing social inequalities and ensuring that the benefits of economic growth are shared by all segments of society. | Positive: Social equity can promote social cohesion, reduce poverty, and create a more inclusive and prosperous society. |
| Environmental Sustainability: Prioritizing environmental protection and sustainable development practices to ensure the long-term health and prosperity of the country. | Positive: Sustainable development can protect natural resources, reduce pollution, and create a more resilient and sustainable economy. |
Summary
As Sri Lanka stands at a crossroads, the presidential election presents a critical opportunity for the nation to turn the tide on its economic woes. The outcome will not only determine the leadership of the country but also shape its path to recovery.
The election will be a test of the electorate’s resolve to choose a leader who can deliver on the promises of economic stability and prosperity, ultimately deciding the future of Sri Lanka.
Top FAQs: Sri Lankans Vote In A Presidential Election That Will Decide How It Recovers From Economic Crisis
What are the main candidates’ economic recovery plans?
Each candidate has Artikeld their approach to addressing the economic crisis, focusing on areas like debt restructuring, attracting foreign investment, boosting exports, and promoting domestic production. The specifics of their plans vary, with some emphasizing fiscal austerity and others prioritizing social welfare programs.
How has the economic crisis impacted ordinary Sri Lankans?
The economic crisis has had a profound impact on ordinary Sri Lankans, leading to rising costs of living, shortages of essential goods like fuel and medicine, and widespread unemployment. Many families are struggling to make ends meet, and there’s growing concern about food insecurity and access to healthcare.
What role has international support played in the crisis?
International organizations like the IMF and World Bank, along with countries like India and China, have provided financial assistance and support to Sri Lanka. This aid has helped to alleviate the immediate pressure on the economy, but it’s crucial to address the underlying structural issues to ensure long-term sustainability.
 CentralPoint Latest News
CentralPoint Latest News