Asia FX rises as rate cut dents dollar; yen firms as BOJ holds course – Asia FX Rises, Dollar Weakened by Rate Cut, Yen Firm as BOJ Holds Course: The global financial landscape shifted dramatically this week as the US Federal Reserve implemented a rate cut, sending the dollar tumbling and Asian currencies soaring.
Meanwhile, the Bank of Japan’s decision to maintain its current monetary policy propelled the yen higher, defying expectations and leaving investors with a complex mix of opportunities and challenges.
This unexpected move by the US Federal Reserve, aimed at stimulating economic growth, triggered a wave of speculation across financial markets. The dollar, weakened by the rate cut, lost ground against most major currencies, particularly those in Asia. The region’s economies, already buoyed by strong fundamentals, were further emboldened by the prospect of a weaker dollar, creating a favorable environment for exports and investment.
Asia FX Gains: Asia FX Rises As Rate Cut Dents Dollar; Yen Firms As BOJ Holds Course
The US dollar experienced a decline as the Federal Reserve opted for a rate cut, prompting a surge in Asian currencies. This move, aimed at bolstering the US economy, had the unintended consequence of weakening the dollar’s appeal to investors.
The rate cut, combined with other factors, contributed to the strengthening of Asian currencies.
Factors Driving Asian Currency Gains
The rate cut by the Federal Reserve played a significant role in the rise of Asian currencies. The decision to lower interest rates made the dollar less attractive to investors seeking higher returns, leading to a decrease in demand for the US currency.
Consequently, the dollar weakened against other currencies, including those in Asia.Furthermore, the Bank of Japan’s decision to maintain its current monetary policy, including its ultra-loose stance, provided further support for Asian currencies. The BOJ’s commitment to keeping interest rates low and engaging in aggressive quantitative easing has made the yen less attractive to investors seeking higher returns.
This has resulted in a weaker yen, which in turn has boosted other Asian currencies.
Examples of Asian Currency Strength
Several Asian currencies have witnessed significant gains against the US dollar in recent times. Notably, the South Korean won has strengthened by over 2% against the dollar, while the Indonesian rupiah has appreciated by more than 1%. The Philippine peso and the Thai baht have also recorded notable gains, reflecting the broader trend of Asian currency appreciation.
Impact of Rate Cut on Future Currency Movements
The recent rate cut by the Federal Reserve is likely to have a significant impact on future currency movements. With interest rates in the US now lower, investors may be less inclined to hold dollar-denominated assets, potentially leading to further depreciation of the US currency.
Conversely, Asian currencies, which are generally perceived as offering higher returns, may continue to appreciate.However, it’s important to note that the future trajectory of currency movements is influenced by a multitude of factors, including global economic conditions, geopolitical events, and market sentiment.
Therefore, while the rate cut has created a favorable environment for Asian currencies, their future performance will depend on the interplay of these various factors.
Japanese Yen Strength
The Japanese yen has strengthened against the US dollar and other major currencies, bucking the trend of most other Asian currencies. This unexpected resilience is largely attributed to the Bank of Japan’s (BOJ) decision to maintain its ultra-loose monetary policy, a stark contrast to the tightening measures adopted by other central banks globally.
You also can understand valuable knowledge by exploring Ibex Ltd executives sell over $680k in company shares.
The Bank of Japan’s Decision
The BOJ’s decision to hold its course on monetary policy, despite rising inflation, has been a key factor behind the yen’s recent strength. The central bank has maintained its yield curve control (YCC) policy, which aims to keep interest rates at ultra-low levels.
This decision reflects the BOJ’s commitment to supporting economic growth, even as inflation rises.
Potential Implications of the BOJ’s Decision
The BOJ’s continued easing stance, despite global tightening trends, has created a significant divergence in monetary policy between Japan and other major economies. This divergence has made the yen more attractive to investors seeking higher returns, leading to a strengthening of the currency.
Comparison with Other Major Currencies
The yen’s performance against other major currencies has been particularly noteworthy. It has gained significantly against the US dollar, which has been weakened by the Federal Reserve’s aggressive rate hikes. The yen has also strengthened against the euro and the British pound, which have been affected by economic uncertainty in their respective regions.
Factors Contributing to the Yen’s Strength
Several factors have contributed to the yen’s recent strength:
- The BOJ’s decision to maintain its ultra-loose monetary policy has created a yield differential between Japan and other major economies, making the yen more attractive to investors seeking higher returns.
- The yen is often seen as a safe-haven currency during periods of global economic uncertainty. As the world grapples with inflation, geopolitical tensions, and a potential recession, investors have flocked to the yen as a safe haven.
- Japan’s current account surplus has also supported the yen. The surplus reflects the country’s strong export performance and limited reliance on imports.
Market Reactions
The US Federal Reserve’s decision to cut interest rates and the Bank of Japan’s (BOJ) commitment to maintaining its ultra-loose monetary policy sent shockwaves through global financial markets, triggering a wave of volatility across asset classes.
Impact on Global Financial Markets
The US rate cut, aimed at mitigating the economic slowdown caused by the ongoing trade war and global uncertainties, spurred a rally in global equity markets. Investors interpreted the move as a sign of easing monetary policy, which is generally considered favorable for economic growth and corporate earnings.
However, the yen’s appreciation against the dollar, driven by the BOJ’s decision to maintain its current policy stance, created a mixed bag for investors. The yen’s strength could potentially hurt Japanese exporters, who rely on a weaker currency to boost their competitiveness in global markets.
Outlook for Asia’s Economic Growth
The diverging monetary policies of the US and Japan highlight the complexities of navigating the global economic landscape. While the US rate cut aims to stimulate economic growth, the BOJ’s stance reflects its concerns about deflationary pressures and the need to support domestic demand.
The impact of these policies on Asia’s economic growth remains uncertain. The region’s economies are heavily reliant on exports, and a weakening dollar could potentially boost demand for Asian goods. However, the trade war and global uncertainties continue to weigh on the outlook.
Implications for Investors and Businesses, Asia FX rises as rate cut dents dollar; yen firms as BOJ holds course
Investors are grappling with the implications of these divergent monetary policies for their portfolios. The yen’s appreciation could create opportunities for investors seeking exposure to Japanese assets, while the US rate cut could lead to a reassessment of risk appetite and potentially higher valuations for US equities.
Businesses operating in Asia are navigating the challenges of currency fluctuations and global trade tensions. The yen’s strength could make Japanese exports less competitive, while the trade war could disrupt supply chains and create uncertainty for businesses operating across borders.
Economic Context
Asia’s economic landscape is currently characterized by a mix of growth and challenges. While some economies are experiencing robust expansion, others face headwinds from global economic uncertainties and rising inflation. This complex interplay of factors shapes the region’s economic outlook and influences currency movements.
Key Economic Factors in Asia
The economic outlook for Asia is influenced by several key factors:
- China’s Economic Performance:China, being the region’s economic powerhouse, significantly impacts Asia’s growth trajectory. Its economic performance, including its post-pandemic recovery, will have a ripple effect on other Asian economies.
- Global Inflation and Interest Rates:Rising inflation and aggressive interest rate hikes by major central banks pose a risk to Asian economies. Higher borrowing costs could dampen investment and economic growth.
- Supply Chain Disruptions:The ongoing global supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by the Russia-Ukraine conflict, have impacted manufacturing and trade in Asia.
- Geopolitical Tensions:Escalating geopolitical tensions, particularly in the Indo-Pacific region, could create uncertainty and affect economic activity.
Relationship Between Interest Rates and Currency Movements
Interest rates play a crucial role in influencing currency movements. Generally, higher interest rates attract foreign investment, boosting demand for the currency and causing it to appreciate. Conversely, lower interest rates can lead to capital outflows, weakening the currency.
For example, if a country’s central bank raises interest rates, it becomes more attractive for investors to park their money in that country, leading to an increase in demand for its currency. This, in turn, appreciates the currency’s value.
Impact of Global Economic Trends on Asia
Global economic trends have a significant impact on Asia’s economies. For instance, a global recession could lead to reduced demand for Asian exports, slowing economic growth in the region. Similarly, a surge in commodity prices due to global supply chain disruptions could fuel inflation in Asia.
Currency Trading Strategies
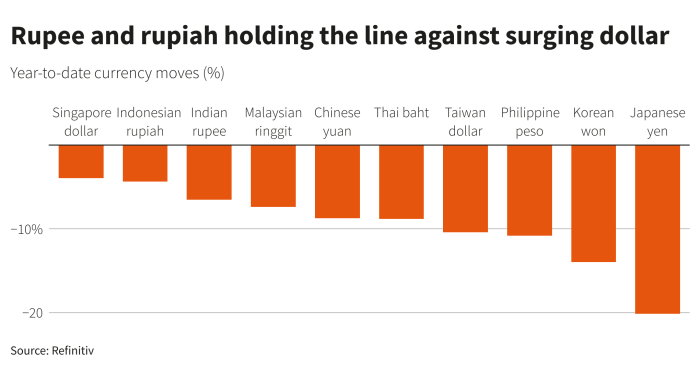
The recent movements in Asian currencies, driven by factors such as interest rate differentials and economic growth prospects, present both opportunities and challenges for currency traders. Understanding the market dynamics and employing appropriate trading strategies can help navigate these fluctuations effectively.
Trading Strategies for Asian Currencies
This section Artikels potential trading strategies that leverage the current market conditions and address the specific characteristics of Asian currencies.
- Carry Trade:This strategy involves borrowing in a low-interest-rate currency and investing in a high-interest-rate currency. In the current scenario, with the US Federal Reserve expected to continue raising interest rates, the Japanese yen, with its ultra-low interest rates, could be a suitable borrowing currency.
Conversely, currencies like the Indonesian rupiah or the Philippine peso, with higher interest rates, could be attractive investment options. However, it’s crucial to consider the risks associated with carry trades, such as potential currency depreciation and widening interest rate differentials.
- Trend Following:This strategy involves identifying and riding established trends in currency prices. For instance, if the Japanese yen is strengthening against the US dollar, a trend-following strategy would involve buying yen and selling dollars, aiming to profit from the ongoing appreciation of the yen.
Technical indicators, such as moving averages and momentum oscillators, can be helpful in identifying trends.
- Mean Reversion:This strategy focuses on exploiting temporary deviations from the historical average price of a currency pair. For example, if the Singapore dollar weakens sharply against the US dollar, a mean reversion strategy might involve buying Singapore dollars and selling US dollars, anticipating that the Singapore dollar will eventually revert back to its historical average.
Risks and Opportunities in Trading Asian Currencies
Trading Asian currencies presents both opportunities and risks that traders must carefully consider.
- Volatility:Asian currencies are known for their volatility, which can be attributed to factors such as political instability, economic uncertainty, and global market events. This volatility can create opportunities for significant profits, but it also increases the risk of losses.
- Interconnectedness:Asian economies are interconnected, and events in one country can have a ripple effect on others. For example, a slowdown in China’s economy could negatively impact currencies across the region. This interconnectedness requires traders to consider the broader regional context when making trading decisions.
- Intervention:Central banks in Asia sometimes intervene in the currency markets to manage exchange rates. This intervention can significantly impact currency movements, creating unexpected price swings. Traders must be aware of potential intervention policies and their impact on their trading strategies.
Technical and Fundamental Analysis for Currency Trading
Both technical and fundamental analysis play crucial roles in making informed trading decisions.
- Technical Analysis:This approach uses historical price data and chart patterns to identify trends and predict future price movements. Technical indicators, such as moving averages, MACD, and RSI, can be helpful in analyzing price patterns and identifying potential buy or sell signals.
- Fundamental Analysis:This approach focuses on economic factors that influence currency values, such as interest rates, inflation, economic growth, and government policies. By analyzing these factors, traders can assess the underlying strength or weakness of a currency and make informed trading decisions.
Risk Management in Currency Trading
Effective risk management is crucial for success in currency trading.
- Stop-Loss Orders:These orders automatically exit a trade when a predetermined price level is reached, limiting potential losses.
- Position Sizing:This involves determining the appropriate size of a trade based on risk tolerance and account balance.
- Diversification:Spreading investments across different currency pairs can help reduce overall risk.
Conclusive Thoughts
As the dust settles, the impact of these developments on Asia’s economic trajectory remains a subject of intense debate. While the weaker dollar presents a potential boon for exporters, the yen’s surprising strength raises questions about the future direction of Japanese monetary policy.
Investors and businesses alike are grappling with the implications of these shifts, seeking to navigate a landscape characterized by uncertainty and volatility. The coming weeks will be crucial in determining the long-term consequences of these decisions, shaping the future of Asia’s economic landscape and the global financial order.
FAQ Guide
What are the potential risks associated with trading Asian currencies?
Trading Asian currencies involves inherent risks, including volatility, currency fluctuations, and geopolitical events. It is crucial to conduct thorough research, understand the market dynamics, and implement appropriate risk management strategies.
How might the rate cut affect future currency movements?
The rate cut could further weaken the dollar in the short term, potentially boosting Asian currencies. However, long-term impacts depend on various factors, including economic growth, inflation, and geopolitical developments.
What are the key factors influencing Asia’s economic outlook?
Asia’s economic outlook is influenced by factors such as global trade, technological advancements, domestic consumption, and government policies. Strong fundamentals and robust growth in key economies like China and India provide a positive outlook for the region.
 CentralPoint Latest News
CentralPoint Latest News