BOJ holds interest rates, flags steady growth in inflation, a decision that sends ripples through the global financial landscape. The Bank of Japan’s move to maintain interest rates at their current levels, despite rising inflation, signals a cautious approach to managing economic growth in the face of global uncertainties.
This decision, coupled with the acknowledgment of steady inflation, raises questions about the BOJ’s long-term strategy and its potential impact on the Japanese economy.
The decision to hold rates comes as Japan grapples with a complex economic landscape. While inflation is rising, it remains relatively subdued compared to other major economies. This presents the BOJ with a delicate balancing act: maintaining a loose monetary policy to stimulate growth while keeping inflation in check.
The bank’s outlook on inflation, acknowledging its steady rise, indicates a shift in their previous stance of keeping inflation below 2%. This shift reflects the growing influence of global factors, including supply chain disruptions and energy price hikes, on Japan’s economy.
BOJ’s Decision to Hold Interest Rates
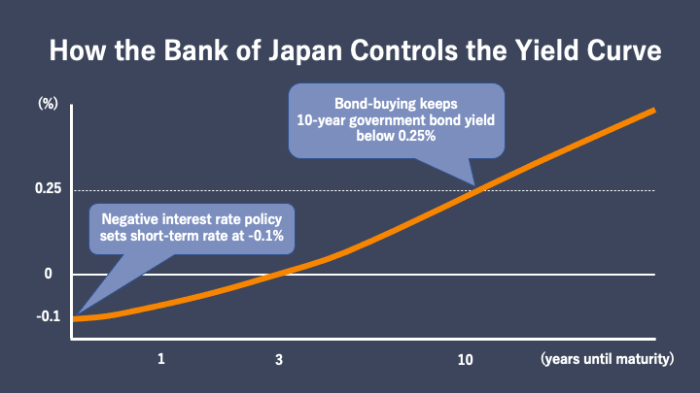
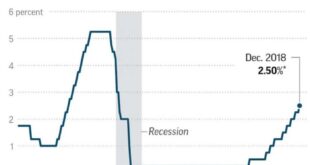
The Bank of Japan (BOJ) has once again opted to keep interest rates unchanged, marking a significant divergence from the global trend of central banks raising rates to combat inflation. This decision, while seemingly at odds with the current economic landscape, reflects a careful consideration of Japan’s unique economic circumstances and the potential implications of altering its monetary policy.
Reasons Behind the BOJ’s Decision
The BOJ’s decision to maintain its ultra-loose monetary policy is driven by several factors. Primarily, the Japanese economy is grappling with persistent deflation, a situation characterized by falling prices and sluggish demand. This contrasts sharply with the inflationary pressures experienced by other major economies.
The BOJ believes that raising interest rates could exacerbate deflationary pressures, potentially leading to a prolonged economic downturn.Additionally, the BOJ’s decision is influenced by Japan’s structural economic challenges, including a rapidly aging population and a shrinking workforce. These factors contribute to weak economic growth and limit the effectiveness of conventional monetary policy tools.
The BOJ’s continued commitment to its yield curve control (YCC) policy, which aims to keep long-term interest rates near zero, reflects its efforts to stimulate investment and economic activity.
Potential Economic Implications
The BOJ’s decision to hold interest rates carries both potential benefits and risks for the Japanese economy. On the positive side, maintaining low interest rates could encourage investment and borrowing, stimulating economic growth. Additionally, it could help to maintain the value of the Japanese yen, which has been under pressure due to the widening interest rate differential with other major currencies.However, there are also potential downsides to the BOJ’s approach.
Keeping interest rates low for an extended period could lead to asset bubbles and financial instability. Moreover, it could further weaken the yen, making imports more expensive and potentially fueling inflation. The BOJ’s decision to maintain its current course will likely be scrutinized closely by economists and investors, who will be watching for any signs of economic weakness or inflationary pressures that could force the BOJ to reconsider its stance.
Comparison with Other Central Banks, BOJ holds interest rates, flags steady growth in inflation
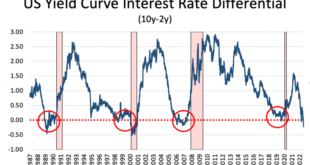
The BOJ’s decision to maintain its ultra-loose monetary policy stands in stark contrast to the actions of other major central banks, such as the Federal Reserve (Fed) and the European Central Bank (ECB). These institutions have been aggressively raising interest rates in an effort to combat inflation.
The BOJ’s divergent approach highlights the unique challenges faced by the Japanese economy and the complexities of managing monetary policy in a globalized world.
Inflation Outlook and Projections: BOJ Holds Interest Rates, Flags Steady Growth In Inflation
The Bank of Japan (BOJ) maintained its ultra-loose monetary policy, holding interest rates steady despite the recent surge in inflation. While the BOJ acknowledged the persistent inflationary pressures, it emphasized its commitment to achieving its 2% inflation target sustainably and in a stable manner.
This decision reflects the BOJ’s assessment of the current economic situation and its outlook for inflation.
Inflation Trends and Contributing Factors
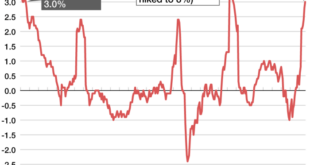
Japan’s inflation has been steadily rising, driven by a combination of factors. The consumer price index (CPI) excluding fresh food, a key measure of inflation, rose by 3.8% in June 2023, the highest level in over four decades. This persistent upward trend is primarily attributed to several factors:
- Supply Chain Disruptions:The ongoing global supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic and the war in Ukraine, have led to higher input costs for businesses, which they have passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
- Energy Prices:The surge in global energy prices, fueled by the war in Ukraine and the subsequent sanctions on Russia, has significantly impacted Japan’s import costs. The sharp increase in energy prices has contributed to higher inflation across various sectors, including transportation and manufacturing.
- Consumer Demand:The gradual recovery of the Japanese economy from the pandemic has led to an increase in consumer demand, which has put upward pressure on prices for goods and services.
BOJ’s Inflation Projections
The BOJ’s projections for future inflation remain cautiously optimistic, but acknowledge the persistent inflationary pressures. The central bank expects inflation to moderate in the coming months, but remain above its 2% target for the remainder of fiscal year 2023. The BOJ’s forecasts are based on the assumption that the current supply chain disruptions will gradually ease, energy prices will stabilize, and the Japanese economy will continue to recover.
Risks to Inflation Projections
Despite the BOJ’s optimistic outlook, there are several risks to its inflation projections. The ongoing geopolitical uncertainties, particularly the war in Ukraine, could lead to further disruptions in global supply chains and higher energy prices. Additionally, the BOJ’s projections are based on the assumption that the Japanese economy will continue to recover at a steady pace, which could be disrupted by unforeseen events, such as a new wave of COVID-19 infections or a global economic slowdown.
Impact on Japanese Economy
The BOJ’s decision to maintain interest rates while acknowledging rising inflation presents a complex scenario for the Japanese economy. While the move aims to support economic growth, it also necessitates careful navigation of the potential consequences of sustained inflation.
Growth Prospects and Investment
The BOJ’s decision to keep interest rates low is intended to stimulate economic activity by making borrowing more affordable for businesses and consumers. This could potentially lead to increased investment, particularly in sectors like infrastructure and technology, which are crucial for long-term economic growth.
However, the effectiveness of this strategy hinges on factors like consumer confidence, business sentiment, and the overall global economic environment. If these factors remain uncertain, the impact of low interest rates on investment may be limited.
Consumer Spending and Inflation
Sustained inflation poses a significant challenge to the Japanese economy, particularly in terms of consumer spending. Rising prices for essential goods and services can erode purchasing power, leading to a decline in consumer confidence and a decrease in overall demand.
This could have a cascading effect on businesses, potentially leading to reduced investment and job creation. The BOJ’s strategy for managing inflation while maintaining economic growth involves a delicate balancing act.
BOJ’s Strategy for Managing Inflation
The BOJ’s approach to managing inflation focuses on a combination of monetary policy and fiscal measures. By keeping interest rates low, the BOJ aims to encourage borrowing and spending, while also monitoring inflation closely. The government’s fiscal policy, including targeted subsidies and support programs, plays a crucial role in mitigating the impact of inflation on vulnerable households and businesses.
However, the effectiveness of these measures depends on factors like the severity and duration of inflation, as well as the government’s ability to implement these policies effectively.
Global Economic Context
The BOJ’s decision to hold interest rates while other major central banks are aggressively raising rates reflects the unique challenges facing the Japanese economy. While inflation is rising globally, Japan’s inflation rate remains relatively low, and the country’s economy is still recovering from the pandemic.
The Global Economic Landscape
The global economy is facing a confluence of challenges, including rising inflation, supply chain disruptions, and the ongoing war in Ukraine. These factors have led many central banks to raise interest rates to curb inflation, but the BOJ’s decision to maintain its accommodative monetary policy highlights the divergence in economic conditions across the globe.
Discover the crucial elements that make Nvidia’s principal accounting officer sells shares worth over $520,000 the top choice.
The BOJ’s decision reflects its commitment to supporting economic growth, even as other central banks prioritize fighting inflation.
Comparing Japan’s Economic Challenges
While other major economies are grappling with high inflation, Japan’s inflation rate remains relatively low. This is partly due to the country’s unique economic structure, which is heavily reliant on exports and has a large domestic savings rate. Japan’s economy is also still recovering from the pandemic, and the BOJ is concerned that raising interest rates could stifle growth.
Potential Spillover Effects
The BOJ’s decision to hold interest rates could have spillover effects on global financial markets and trade. For example, the yen could depreciate further against other currencies, making Japanese exports more competitive but also increasing the cost of imports. The BOJ’s decision could also lead to increased volatility in global financial markets, as investors adjust to the divergent monetary policies of different countries.
Final Conclusion
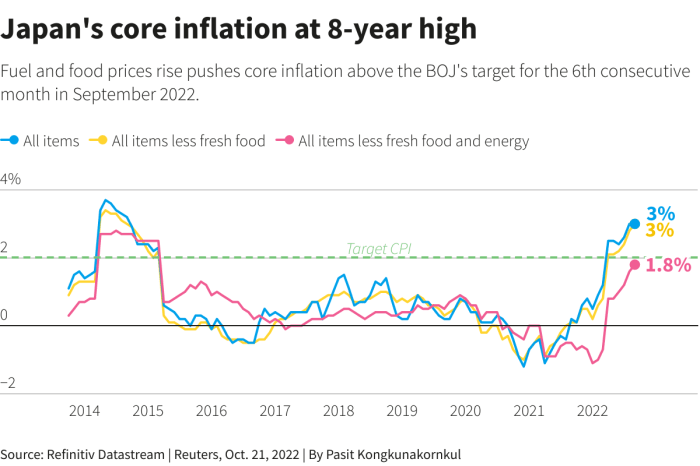
The BOJ’s decision to hold interest rates while acknowledging the steady rise in inflation reflects the complex economic challenges Japan faces. This strategic move positions the BOJ to navigate the global economic landscape with a cautious approach, balancing growth and stability in a world of rising inflation and global uncertainty.
The implications of this decision on the Japanese economy, both in the short and long term, remain to be seen, but it is clear that the BOJ is carefully monitoring the situation and adjusting its policies accordingly. The path forward for Japan’s economy will be influenced by the global economic landscape, and the BOJ’s actions will play a crucial role in shaping the nation’s economic trajectory.
User Queries
What are the potential consequences of sustained inflation on the Japanese economy?
Sustained inflation could lead to a decrease in purchasing power, potentially impacting consumer spending and economic growth. It could also strain businesses and individuals with existing debt, increasing the cost of borrowing and potentially leading to financial instability. Additionally, it could impact wage negotiations, as workers demand higher salaries to keep pace with rising prices.
How does the BOJ’s decision compare to other major central banks?
The BOJ’s decision to hold interest rates stands in contrast to many other major central banks, which have been raising interest rates aggressively to combat inflation. This divergence in monetary policy reflects the unique economic challenges faced by Japan, including a relatively low inflation rate and a dependence on exports.
The BOJ’s cautious approach aims to avoid stifling economic growth while keeping inflation under control.
What are the potential spillover effects of the BOJ’s decision on global financial markets and trade?
The BOJ’s decision could have ripple effects on global financial markets and trade. Maintaining low interest rates in Japan could attract investment capital seeking higher returns, potentially impacting currency exchange rates and influencing global capital flows. Additionally, the BOJ’s approach could influence the policies of other central banks and impact global trade patterns.
 CentralPoint Latest News
CentralPoint Latest News