Barclays doubts the Fed will cut as much as currently priced in, a bold statement that throws a wrench into the market’s optimistic outlook. While investors eagerly anticipate significant rate reductions, Barclays argues that the current economic environment doesn’t warrant such aggressive easing.
This contrarian view sparks intrigue, prompting a closer look at the reasoning behind Barclays’ skepticism and the potential implications for financial markets.
The crux of Barclays’ argument lies in their assessment of inflation, which they believe will remain stubbornly persistent. They foresee the Fed, despite recent hawkish rhetoric, remaining cautious in its approach to rate cuts, prioritizing price stability over stimulating economic growth.
This perspective clashes with the market’s expectation of a swift and substantial easing cycle, creating a fascinating tug-of-war between optimism and caution.
Barclays’ Viewpoint: Barclays Doubts The Fed Will Cut As Much As Currently Priced In
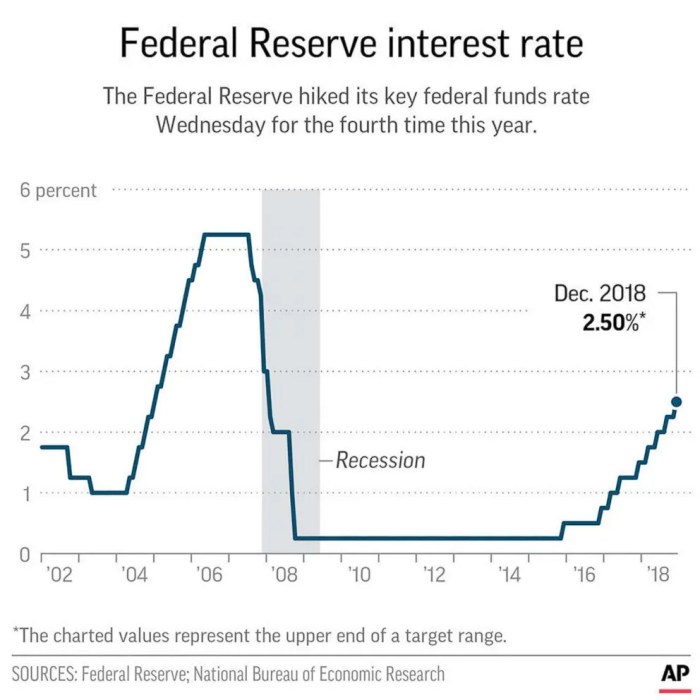
Barclays, a prominent financial institution, has expressed skepticism regarding the market’s current expectation of substantial interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve. The investment bank believes that the Fed might not be as aggressive in easing monetary policy as the market anticipates, leading to a potential divergence between market expectations and the Fed’s actual actions.
Barclays’ Reasoning for Doubting Significant Rate Cuts, Barclays doubts the Fed will cut as much as currently priced in
Barclays’ reasoning for doubting the market’s expectation of significant rate cuts stems from its assessment of the current economic environment and its outlook for inflation. The investment bank believes that the recent decline in inflation is likely to be temporary and that core inflation will remain elevated.
This perspective suggests that the Fed might be less inclined to cut rates aggressively, as they could be concerned about reigniting inflationary pressures.
Barclays’ Assessment of the Current Economic Environment
Barclays believes that the current economic environment is characterized by a resilient labor market, strong consumer spending, and continued business investment. The bank acknowledges that the recent rise in interest rates has had a cooling effect on economic activity, but it argues that this impact has been relatively modest.
Barclays believes that the economy is likely to continue growing, albeit at a slower pace, in the coming months.
Barclays’ Forecast for Inflation and its Impact on Monetary Policy
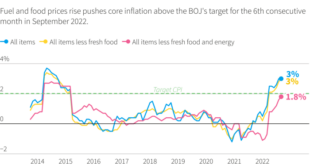
Barclays forecasts that inflation will remain elevated in the near term, driven by factors such as tight labor markets and supply chain disruptions. The bank expects core inflation to remain above the Fed’s 2% target for an extended period. This outlook suggests that the Fed might be reluctant to cut rates aggressively, as doing so could lead to a resurgence of inflationary pressures.
Market Expectations
The market currently anticipates that the Federal Reserve will pivot towards a more accommodative stance in the coming months, with expectations for rate cuts already baked into financial markets. This sentiment is driven by a confluence of factors, including concerns about a potential economic slowdown, easing inflationary pressures, and the Fed’s own communication.
Extent of Rate Cuts Priced In
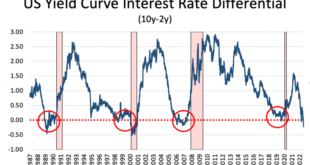
The market is pricing in a significant degree of rate cuts in the coming months. The CME FedWatch Tool, a popular gauge of market expectations, currently suggests a high probability of at least one rate cut by the end of the year, with some investors even anticipating multiple cuts.
This is a stark contrast to the Fed’s own projections, which currently indicate that interest rates will remain elevated for a prolonged period.
Key Factors Driving Market Expectations
Several factors are contributing to the market’s expectation of rate cuts. These include:
- Slowing Economic Growth:Recent economic data has pointed to a slowdown in economic activity, raising concerns about a potential recession. The Fed’s own projections have also been revised downwards, indicating a less optimistic outlook for growth.
- Easing Inflationary Pressures:While inflation remains elevated, it has shown signs of cooling in recent months. This has led some investors to believe that the Fed may have more room to maneuver on interest rates.
- Fed Communication:The Fed’s recent communication has been interpreted by some as signaling a potential shift in policy. While the Fed has maintained its commitment to fighting inflation, it has also acknowledged the possibility of a slowdown in the economy.
Barclays’ Viewpoint
Barclays’ view differs from the prevailing market sentiment. The firm believes that the Fed will be reluctant to cut rates in the near term, citing the ongoing battle against inflation and the need to maintain restrictive monetary policy for a sustained period.
Barclays argues that the market is underestimating the Fed’s commitment to bringing inflation down to its 2% target.
Economic Data and Indicators
The recent economic data paints a mixed picture, making it difficult for the Fed to confidently predict the future path of interest rates. While some indicators suggest a resilient economy, others point to potential vulnerabilities that could warrant a more cautious approach.
Inflation Trends
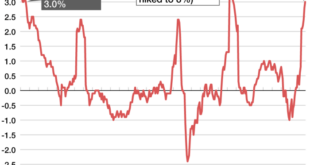
Inflation has been a major concern for the Fed, and recent data has shown some signs of moderation. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose 3.0% year-over-year in June, down from 4.0% in May, indicating a continued slowdown in price increases.
Check Warburg Pincus entities sell $10.2 million in Ring Energy stock to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
However, core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, remained elevated at 4.8%, suggesting that underlying price pressures persist. This data suggests that inflation is gradually easing, but it remains a key factor influencing the Fed’s policy decisions.
Labor Market Performance
The labor market remains strong, with unemployment at a historically low level. The unemployment rate fell to 3.6% in June, indicating a tight labor market with ample job opportunities. However, wage growth has shown signs of cooling, with average hourly earnings rising by 4.4% year-over-year in June, down from 4.6% in May.
This slowdown in wage growth could signal a potential easing of inflationary pressures.
GDP Growth
The U.S. economy grew at an annualized rate of 2.0% in the first quarter of 2023, a significant slowdown from the previous quarter’s 2.6% growth. This suggests that economic activity is slowing, potentially due to higher interest rates and persistent inflation.
The Fed closely monitors GDP growth as a key indicator of the overall health of the economy.
The Fed’s Policy Stance
The Federal Reserve (Fed) is the central bank of the United States, responsible for maintaining price stability and promoting maximum employment. It achieves this through its monetary policy tools, primarily by adjusting interest rates and managing the money supply. The Fed’s policy stance reflects its assessment of the current economic conditions and its outlook for the future.The Fed’s recent communication has highlighted its commitment to fighting inflation, even at the cost of some economic slowdown.
While the Fed acknowledges the risks of a recession, it believes that bringing inflation under control is paramount for long-term economic stability.
The Fed’s Communication Regarding Inflation and Economic Growth
The Fed’s communication regarding inflation and economic growth has been characterized by a cautious optimism. While acknowledging the recent easing of inflationary pressures, the Fed remains vigilant in its efforts to bring inflation down to its 2% target. The Fed’s statements have emphasized the need for continued rate hikes and a sustained period of restrictive monetary policy to ensure that inflation remains on a downward trajectory.
The Fed’s recent communication has also highlighted the ongoing uncertainty surrounding the economic outlook. While the labor market remains strong, there are signs that economic growth is slowing, driven by factors such as rising interest rates and persistent inflation. The Fed is closely monitoring these developments and stands ready to adjust its policy stance if necessary.
The Fed’s Approach to Managing Inflation and Achieving Price Stability
The Fed’s approach to managing inflation and achieving price stability is based on a framework that emphasizes the importance of maintaining price stability as a foundation for sustainable economic growth. The Fed’s primary tool for controlling inflation is the federal funds rate, which is the target rate for overnight lending between banks.
By raising the federal funds rate, the Fed makes it more expensive for banks to borrow money, which in turn slows down economic activity and reduces inflationary pressures.The Fed also uses other tools to manage inflation, such as adjusting the reserve requirements for banks and buying or selling government bonds.
The Fed’s actions in these areas can influence the amount of money in circulation, which can also impact inflation.
The Fed’s Potential Policy Options and Their Implications for the Economy
The Fed’s potential policy options include continuing to raise interest rates, pausing rate hikes, or even cutting interest rates. The decision on which path to take will depend on the Fed’s assessment of the economic outlook, including inflation, economic growth, and the labor market.
Continuing to Raise Interest Rates
Continuing to raise interest rates would further tighten monetary policy, slowing down economic activity and potentially increasing the risk of a recession. However, it would also help to bring inflation down more quickly.
Pausing Rate Hikes
Pausing rate hikes would allow the Fed to assess the impact of its previous rate increases on the economy. This could provide more time for inflation to moderate and for the economy to adjust to the higher interest rate environment.
Cutting Interest Rates
Cutting interest rates would loosen monetary policy, stimulating economic activity and potentially boosting inflation. However, it would also increase the risk of inflation remaining high or even accelerating.The Fed’s decision on its future policy path will be closely watched by investors and policymakers alike.
The Fed’s actions will have significant implications for the economy, including interest rates, inflation, and economic growth.
Impact on Financial Markets
Barclays’ skepticism regarding the Federal Reserve’s commitment to aggressive rate cuts could significantly impact financial markets, influencing investor sentiment and potentially altering asset prices. This viewpoint challenges the prevailing market expectations, which anticipate a more dovish stance from the Fed, leading to potential shifts in risk appetite and market volatility.
Investor Sentiment and Risk Appetite
Barclays’ view, if widely adopted, could dampen investor optimism and lead to a shift towards a more cautious approach to risk-taking. This could be reflected in a decrease in appetite for riskier assets like stocks and emerging market bonds, as investors become more hesitant about the future trajectory of interest rates.
Conversely, investors may seek refuge in safe-haven assets like US Treasury bonds, driving their prices up and yields down.
Potential Implications for Asset Prices
- Stocks:A decline in risk appetite could lead to a correction in stock markets. Investors may sell off equities as they anticipate lower earnings growth due to potentially higher interest rates. The extent of the impact on stock prices would depend on the magnitude of the rate cuts expected by the market and the degree to which Barclays’ view influences market sentiment.
- Bonds:If Barclays’ view gains traction, it could push bond yields higher. This is because investors would demand a higher return for holding bonds if they anticipate less aggressive rate cuts, leading to a decline in bond prices. However, the impact on bond markets could be mitigated by other factors, such as inflation expectations and the global economic outlook.
- Currencies:Barclays’ view could also impact currency markets. If investors believe that the Fed will not cut rates as much as anticipated, it could weaken the US dollar. This is because a lower interest rate differential between the US and other major economies would make the US dollar less attractive to investors.
Conversely, currencies of countries with relatively higher interest rates could strengthen.
Market Volatility and Risk Appetite
Barclays’ doubts about the Fed’s policy stance could increase market volatility as investors adjust their positions based on the evolving expectations. This could lead to more frequent and larger price swings in various asset classes. Furthermore, if Barclays’ view gains significant traction, it could prompt a reassessment of risk appetite among market participants, potentially leading to a more conservative investment approach and a reduction in speculative trading activity.
Last Recap
Barclays’ dissenting view on the Fed’s rate cut trajectory adds a layer of complexity to the already volatile market landscape. While the market anticipates a rapid easing cycle, Barclays’ stance highlights the uncertainties surrounding inflation and its impact on monetary policy.
This clash of perspectives could lead to increased market volatility and shifting investor sentiment, making it crucial for investors to carefully analyze the economic data and the Fed’s communication to navigate this uncertain terrain.
FAQ Guide
What is the current market sentiment regarding the Fed’s future policy moves?
The market is currently anticipating significant rate cuts in the coming months, with investors pricing in a substantial easing cycle. This sentiment is driven by concerns about a potential recession and the desire for lower borrowing costs to stimulate economic growth.
How does Barclays’ view differ from prevailing market expectations?
Barclays believes that the market is overly optimistic about the extent of rate cuts, arguing that inflation will remain a persistent concern and that the Fed will prioritize price stability over stimulating economic growth. This more cautious perspective contrasts with the market’s anticipation of a rapid easing cycle.
 CentralPoint Latest News
CentralPoint Latest News