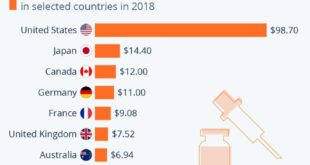
Drug middlemen illegally drive up the cost of insulin, FTC says, exposing a hidden layer of price manipulation in the pharmaceutical supply chain. These middlemen, who act as intermediaries between manufacturers and pharmacies, are accused of exploiting their position to inflate insulin prices, ultimately burdening patients and the healthcare system.
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has launched an investigation into the practices of drug middlemen, alleging that they engage in a complex web of markups and price manipulations that artificially inflate the cost of insulin. This investigation sheds light on the opaque nature of the pharmaceutical supply chain and raises concerns about the ethical and legal implications of these practices.
The Role of Drug Middlemen in the Insulin Market: Drug Middlemen Illegally Drive Up The Cost Of Insulin, FTC Says
Drug middlemen, also known as pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), play a significant role in the pharmaceutical supply chain, including the insulin market. They act as intermediaries between pharmaceutical manufacturers, insurance companies, and pharmacies, negotiating drug prices and managing prescription drug benefits for insurance plans.
Types of Middlemen in the Insulin Market, Drug middlemen illegally drive up the cost of insulin, FTC says
Drug middlemen in the insulin market can be categorized into different types, each with a specific role in the supply chain. These include:
- Pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs): PBMs are the most prominent type of middlemen in the insulin market. They negotiate drug prices with manufacturers, manage formularies (lists of covered drugs), and process prescription claims for insurance plans. They also provide pharmacy networks and mail-order services.
- Wholesale distributors: These middlemen purchase insulin from manufacturers and sell it to pharmacies and other healthcare providers. They manage inventory and ensure the timely delivery of insulin to patients.
- Specialty pharmacies: These pharmacies specialize in dispensing complex medications, including insulin. They often have specialized staff and services to support patients with chronic conditions like diabetes.
Markups Applied by Middlemen
Middlemen in the insulin market apply markups at each stage of the supply chain, contributing to the high cost of insulin for patients.
Obtain access to Top Asian News 4:18 a.m. GMT to private resources that are additional.
- PBMs: PBMs negotiate rebates with manufacturers, which are a percentage of the drug’s price. They can keep a portion of these rebates for themselves and pass on the rest to insurance companies. PBMs also charge administrative fees for processing claims and managing pharmacy networks.
- Wholesale distributors: Wholesale distributors mark up the price of insulin when selling it to pharmacies. These markups are typically a percentage of the wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) of the drug.
- Specialty pharmacies: Specialty pharmacies also apply markups to the price of insulin. These markups can vary depending on the specific pharmacy and the services they provide.
Impact of Middlemen on the Cost of Insulin
The presence of middlemen in the insulin market significantly impacts the cost of insulin for patients.
- Increased drug prices: The markups applied by middlemen at each stage of the supply chain contribute to higher insulin prices for patients. This is particularly true for PBMs, which have been criticized for using their negotiating power to extract higher rebates from manufacturers, which ultimately leads to higher prices for consumers.
- Reduced transparency: The complex nature of the pharmaceutical supply chain, with multiple middlemen involved, can make it difficult for patients to understand the true cost of insulin and how it is being allocated. This lack of transparency can make it challenging for patients to find the most affordable options and negotiate lower prices.
Potential Solutions and Reforms

The issue of drug middlemen driving up the cost of insulin is a complex one, requiring multifaceted solutions to ensure affordability and access for patients. Addressing this issue requires a combination of government regulation, market transparency, and innovative approaches to reduce the role of middlemen in the insulin supply chain.
Government Regulation and Price Controls
Government regulation plays a crucial role in controlling drug prices and middlemen practices. One potential solution is implementing price controls on insulin, similar to those used in other countries. Price controls can limit the profits that pharmaceutical companies and middlemen can make, potentially making insulin more affordable for patients.
Another approach is to increase transparency in the drug pricing system, requiring pharmaceutical companies and middlemen to disclose their pricing and profit margins. This transparency could help identify and address potential price gouging and manipulation.
Alternative Approaches to Affordability
Alternative approaches can also help ensure affordable access to insulin for all patients. One such approach is expanding access to generic insulin. Generic insulin is often significantly cheaper than brand-name insulin, but its availability is limited. Encouraging the development and availability of generic insulin can provide patients with a more affordable option.
Another alternative is to explore government-funded programs that provide subsidized insulin to low-income patients. These programs can ensure that patients who cannot afford insulin have access to this life-saving medication.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Reform Measures
Various reform measures have potential benefits and drawbacks. For example, price controls can make insulin more affordable, but they could also discourage innovation in drug development. Similarly, increasing transparency in pricing can help identify price gouging, but it may also make it more difficult for pharmaceutical companies to recoup their research and development costs.
It is crucial to carefully consider the potential benefits and drawbacks of different reform measures to ensure that any changes made are effective and do not have unintended consequences.
Ending Remarks
The FTC’s investigation into drug middlemen and their role in driving up insulin prices has ignited a debate about the transparency and accountability of the pharmaceutical supply chain. The potential impact on patients, the healthcare system, and the industry itself is significant.
The outcome of this investigation could reshape the insulin market, potentially leading to greater transparency, fairer pricing, and improved access to this life-saving medication.
FAQ Compilation
What are drug middlemen?
Drug middlemen are intermediaries in the pharmaceutical supply chain, acting as brokers between manufacturers and pharmacies. They purchase insulin from manufacturers and then resell it to pharmacies at a markup.
How do drug middlemen allegedly inflate insulin prices?
The FTC alleges that drug middlemen engage in practices like price gouging, market manipulation, and engaging in complex transactions that artificially inflate the cost of insulin.
What are the potential consequences of the FTC’s investigation?
The FTC’s investigation could lead to legal action against drug middlemen, potential regulatory changes to the pharmaceutical supply chain, and ultimately, a shift towards more transparent and affordable insulin pricing.
 CentralPoint Latest News
CentralPoint Latest News