U.S. Rep. Dale Strong calls for new nuclear reactors, names Bellefonte as possible site, igniting a debate about the future of energy in the U.S. Strong’s proposal, which aims to revitalize the nuclear industry, has sparked both enthusiasm and skepticism.
The plan, which would see new reactors built at the former Bellefonte nuclear plant in Alabama, has raised questions about safety, environmental impact, and the overall viability of nuclear power in a rapidly changing energy landscape.
The proposal has generated a mix of reactions. Supporters highlight the potential for clean energy production and economic benefits for the region. Critics, however, voice concerns about the inherent risks associated with nuclear power, including the possibility of accidents and the challenge of managing radioactive waste.
The debate underscores the complex considerations surrounding the role of nuclear energy in the 21st century.
Rep. Strong’s Proposal
U.S. Rep. Dale Strong, representing Alabama’s 5th congressional district, has proposed the construction of new nuclear reactors in the United States, with Bellefonte, Alabama, being a potential site. This proposal, fueled by concerns about energy security and climate change, aims to bolster the country’s energy independence and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Rationale Behind Rep. Strong’s Proposal
Rep. Strong’s proposal is rooted in the belief that nuclear energy plays a vital role in achieving energy independence and mitigating climate change. He emphasizes that nuclear power plants generate clean energy without producing greenhouse gases, making them a crucial component of a sustainable energy future.
Furthermore, Rep. Strong believes that nuclear energy can provide a reliable and consistent energy source, addressing concerns about intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind power.
Benefits Anticipated by Rep. Strong
Rep. Strong anticipates several benefits from his proposal. These include:
- Enhanced Energy Independence:By increasing domestic nuclear power generation, the United States can reduce its reliance on foreign energy sources, improving its energy security and reducing vulnerability to global energy market fluctuations.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions:Nuclear power plants emit significantly fewer greenhouse gases than fossil fuel-based power plants, contributing to efforts to mitigate climate change.
- Economic Growth and Job Creation:The construction and operation of new nuclear power plants would create numerous jobs in various industries, boosting local economies and stimulating economic growth.
- Improved Energy Reliability:Nuclear power plants provide a consistent and reliable energy source, unlike intermittent renewable energy sources, ensuring a stable electricity supply.
Rep. Strong’s Vision for the Future of Nuclear Energy
Rep. Strong envisions a future where nuclear energy plays a central role in the U.S. energy mix. He believes that advancements in nuclear technology, such as the development of small modular reactors (SMRs), will further enhance the safety, efficiency, and affordability of nuclear power.
Rep. Strong’s vision includes a diversified energy portfolio that combines nuclear energy with renewable sources to achieve a sustainable and secure energy future.
Bellefonte Site Selection

The Bellefonte Nuclear Plant, located in Jackson County, Alabama, has a long and complex history. It was originally envisioned as a two-unit plant, but construction began in 1974 and was halted in 1988 due to various factors, including cost overruns and regulatory challenges.
The unfinished plant remains a prominent landmark, but its future is uncertain. Rep. Strong’s proposal to revive the Bellefonte site as a location for new nuclear reactors has sparked renewed interest in the facility’s potential.
Factors Contributing to Bellefonte’s Suitability
The Bellefonte site possesses several characteristics that make it potentially suitable for new nuclear reactors.
- Existing Infrastructure:The site already has extensive infrastructure in place, including cooling towers, a turbine building, and a substantial amount of land. This pre-existing infrastructure could significantly reduce the cost and time required to build new reactors.
- Access to Resources:Bellefonte is located near a major river, providing access to a substantial water source for cooling purposes. The site also has access to transportation networks, including rail lines and highways, which would facilitate the delivery of materials and equipment.
- Skilled Workforce:The region has a skilled workforce with experience in the nuclear industry, having worked at the original Bellefonte plant. This workforce could provide a valuable resource for the construction and operation of new reactors.
- Political Support:The proposal has garnered support from local and state officials, suggesting a positive political environment for the project.
Comparison with Other Potential Locations, U.S. Rep. Dale Strong calls for new nuclear reactors, names Bellefonte as possible site
Comparing Bellefonte to other potential locations for nuclear power plants involves weighing various factors, including:
- Existing Infrastructure:Bellefonte’s existing infrastructure gives it a significant advantage over greenfield sites, which would require extensive construction from scratch.
- Regulatory Environment:The regulatory environment for nuclear power varies across different states. Alabama has a relatively favorable regulatory climate for nuclear power, which could benefit the Bellefonte project.
- Public Acceptance:Public acceptance of nuclear power is a critical factor in the siting process. While the Bellefonte site has faced opposition in the past, recent polls suggest growing support for nuclear energy in Alabama.
- Economic Benefits:The economic benefits of a nuclear power plant, including job creation and tax revenue, can vary depending on the specific location. Bellefonte’s location in a rural area could potentially generate significant economic benefits for the region.
Nuclear Energy in the U.S.: U.S. Rep. Dale Strong Calls For New Nuclear Reactors, Names Bellefonte As Possible Site
Nuclear power generation currently plays a significant role in the U.S. energy landscape, providing a reliable and low-carbon source of electricity. However, the industry faces various challenges and opportunities as it navigates a changing energy landscape.
Current State of Nuclear Power Generation
The U.S. has a long history of nuclear power, with the first commercial reactor coming online in 1957. Today, there are 93 operational nuclear reactors across 55 power plants, generating approximately 20% of the nation’s electricity. This makes the U.S.
the world’s largest producer of nuclear energy. The majority of these reactors are light-water reactors, which use water as a coolant and moderator. However, there are also a few boiling water reactors and a single pressurized water reactor.
Challenges and Opportunities Facing the Nuclear Industry
The nuclear industry faces a number of challenges, including:
- High construction costs:Building new nuclear power plants is expensive, with costs often exceeding initial estimates. This has made it difficult to attract investment for new construction projects.
- Regulatory hurdles:The nuclear industry is subject to stringent safety regulations, which can add to the complexity and cost of building and operating nuclear power plants.
- Public perception:Some people are concerned about the safety of nuclear power plants, particularly in the wake of accidents like Chernobyl and Fukushima. This has led to opposition to new nuclear construction projects.
- Competition from renewable energy:The cost of renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind, has fallen dramatically in recent years, making them increasingly competitive with nuclear power.
Despite these challenges, the nuclear industry also faces a number of opportunities:
- Growing demand for clean energy:As the world transitions to a low-carbon economy, the demand for clean energy sources like nuclear power is expected to increase.
- Advances in technology:New technologies, such as small modular reactors (SMRs), offer the potential for safer, more efficient, and more affordable nuclear power.
- Government support:Some governments, including the U.S. government, are providing financial incentives to support the development and deployment of nuclear power.
Environmental Impact of Nuclear Energy
Nuclear power is a low-carbon source of energy, meaning it does not produce greenhouse gases during operation. This makes it a valuable tool in the fight against climate change.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions:Compared to fossil fuels, nuclear power plants emit significantly less greenhouse gases. While there are emissions associated with the mining and processing of uranium, these emissions are relatively small compared to the emissions from fossil fuel power plants.
- Waste Management:Nuclear power plants produce radioactive waste, which must be carefully managed. This is a significant challenge, but there are technologies available to safely store and dispose of nuclear waste.
- Water Use:Nuclear power plants require significant amounts of water for cooling. This can have an impact on local water resources, particularly in areas with limited water availability.
The environmental impact of nuclear energy is often compared to other energy sources, such as coal, natural gas, and renewable energy.
- Coal:Nuclear power plants emit far fewer greenhouse gases than coal-fired power plants. However, nuclear power plants also produce radioactive waste, which is not produced by coal-fired power plants.
- Natural Gas:Natural gas is a cleaner-burning fuel than coal, but it still emits greenhouse gases. Nuclear power plants produce no greenhouse gases during operation, but they do produce radioactive waste.
- Renewable Energy:Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, are considered to be the cleanest energy sources. However, they are intermittent, meaning they cannot always provide electricity on demand. Nuclear power plants can provide a reliable baseload of electricity, but they do produce radioactive waste.
Technological Advancements in Nuclear Power
The field of nuclear power has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, leading to the development of innovative reactor designs and technologies that promise greater safety, efficiency, and sustainability. These advancements address long-standing concerns about nuclear waste, proliferation risks, and public perception.
Smaller, Safer, and More Efficient Reactors
The development of smaller, safer, and more efficient reactors is a major focus in the nuclear industry. These reactors, often referred to as “small modular reactors” (SMRs), offer several advantages over traditional large-scale reactors.
For descriptions on additional topics like Watch: SuperMotocross World Championship Vegas First Look | TWMX Press Day, please visit the available Watch: SuperMotocross World Championship Vegas First Look | TWMX Press Day.
- Smaller Size and Modular Design:SMRs are significantly smaller than traditional reactors, typically with a power output of less than 300 megawatts. Their modular design allows for factory-built components, which can be transported and assembled on-site, reducing construction time and costs. This modularity also makes them more adaptable to various locations and energy demands.
- Enhanced Safety Features:SMRs incorporate advanced safety features, such as passive cooling systems, which can operate without external power sources. These features significantly reduce the risk of accidents and meltdowns.
- Increased Efficiency:SMRs can achieve higher thermal efficiency than traditional reactors, meaning they can generate more electricity from the same amount of fuel. This increased efficiency reduces fuel consumption and waste generation.
Innovation in Nuclear Waste Disposal
Nuclear waste disposal remains a major concern, but advancements in technology are offering innovative solutions.
- Advanced Reprocessing:Reprocessing techniques are being refined to extract valuable materials from spent nuclear fuel, such as plutonium and uranium. This process reduces the volume of waste and potentially extends the lifespan of nuclear fuel.
- Geological Disposal:Deep geological repositories are being developed to safely and permanently dispose of high-level nuclear waste. These repositories involve storing waste in stable geological formations, such as deep underground rock formations, to prevent its release into the environment.
- Transmutation:Transmutation technologies are being explored to convert long-lived radioactive waste into shorter-lived or non-radioactive elements. This process could significantly reduce the long-term risks associated with nuclear waste.
Last Word
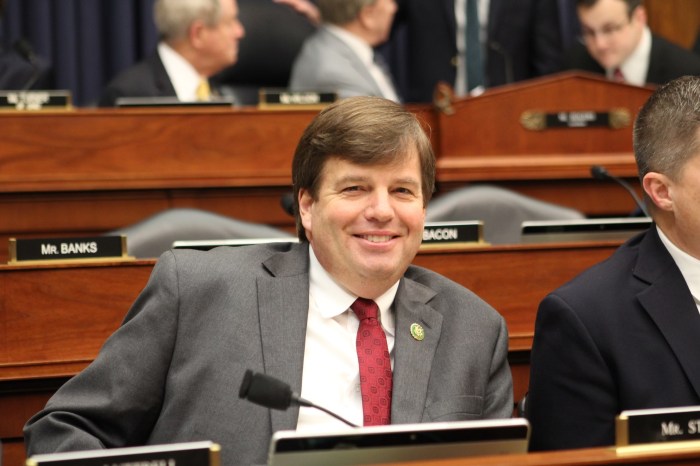

Rep. Strong’s proposal to build new nuclear reactors at the Bellefonte site is a bold move with far-reaching implications. It highlights the ongoing conversation about the future of energy in the U.S., balancing the need for clean energy with the concerns surrounding nuclear power.
Whether or not the project comes to fruition, the debate is likely to continue, shaping the energy landscape for years to come.
Common Queries
What is the current status of the Bellefonte nuclear plant?
The Bellefonte plant was never completed and has been inactive for decades. The site is currently owned by a private company and is being considered for new nuclear reactor construction.
What are the potential economic benefits of building new reactors at Bellefonte?
Proponents argue that the project would create jobs, stimulate economic growth in the region, and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
What are the environmental risks associated with nuclear power?
The potential risks include accidents, radioactive waste disposal, and the possibility of terrorism targeting nuclear facilities.
 CentralPoint Latest News
CentralPoint Latest News