Fed’s Bowman voted against jumbo cut to avoid signaling victory on inflation, a move that highlights the ongoing debate within the Federal Reserve about the appropriate pace of interest rate adjustments. While the majority of policymakers opted for a significant rate cut, Bowman’s dissenting vote underscores the complexities of navigating a volatile economic landscape characterized by persistent inflation concerns.
Bowman’s stance reflects a cautious approach, prioritizing the need to avoid premature declarations of victory over inflation. She argues that such pronouncements could inadvertently fuel inflationary pressures by creating a false sense of security and potentially leading to a relaxation of monetary policy.
Her perspective stands in contrast to the prevailing sentiment within the Fed, which favors a more aggressive approach to combating inflation.
The Context of the Fed’s Decision
The recent decision by the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates by a “jumbo” amount has sparked significant debate among economists and financial analysts. This move comes amidst a backdrop of persistent inflation and a complex economic landscape, raising questions about the Fed’s strategy and its potential impact on the economy.
The Economic Climate and Inflation Concerns
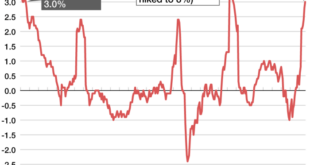
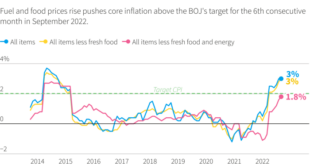
The US economy currently faces a challenging environment marked by persistent inflation. The Consumer Price Index (CPI), a key measure of inflation, has remained stubbornly high, indicating a sustained increase in the cost of goods and services. This inflation has eroded purchasing power for consumers and has put pressure on businesses to raise prices, creating a vicious cycle of rising costs.
The Fed’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability and full employment, making it crucial to address inflation effectively.
The Federal Reserve’s Typical Approach to Interest Rate Adjustments
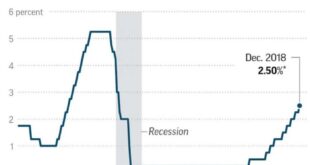
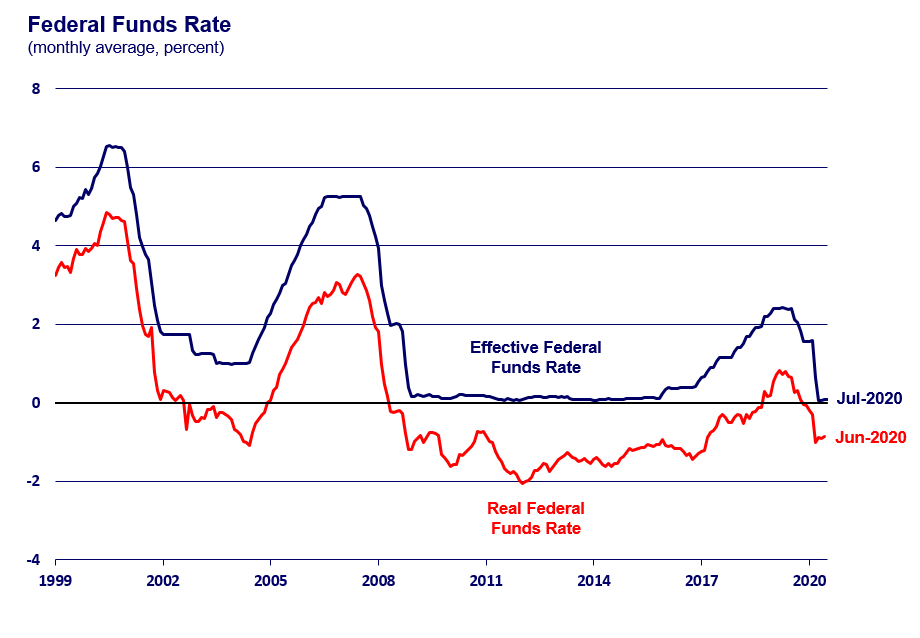
The Federal Reserve typically adjusts interest rates through the federal funds rate, the target rate at which banks lend reserves to each other overnight. This rate serves as a benchmark for other interest rates in the economy. When the Fed wants to stimulate economic growth, it lowers interest rates to encourage borrowing and investment.
Conversely, when it aims to curb inflation, it raises interest rates to make borrowing more expensive and discourage spending. This approach, known as monetary policy, aims to influence the overall level of economic activity and inflation.
Rationale Behind the Recent “Jumbo Cut” and Potential Implications
The recent “jumbo cut” in interest rates reflects the Fed’s assessment of the current economic situation. The decision to lower rates by a significant margin suggests a greater sense of urgency to address the economic slowdown and potentially mitigate the risks of a recession.
The rationale behind this move likely stems from concerns about slowing economic growth, the potential for a recession, and the desire to provide a more substantial boost to the economy. However, this aggressive approach has also sparked debate about the potential consequences.
Some argue that such a large rate cut could exacerbate inflation by making borrowing cheaper and potentially fueling further price increases. Others suggest that it could lead to asset bubbles, where prices in certain markets rise rapidly due to excessive speculation.
The ultimate impact of this decision remains to be seen, but it highlights the complex trade-offs faced by policymakers in navigating the current economic environment.
Bowman’s Dissent
In a rare move, Federal Reserve Governor Michelle Bowman dissented from the decision to lower interest rates by a quarter of a percentage point. Bowman’s dissent highlights a crucial point: the potential risks of prematurely signaling a victory over inflation.
Bowman’s Concerns
Bowman’s dissent stemmed from her concerns about the persistence of inflation and the potential for a premature easing of monetary policy to reignite inflationary pressures. She emphasized that while recent data showed a cooling of inflation, the Fed should remain vigilant and avoid any actions that could be misconstrued as a signal of victory over inflation.
Potential Consequences of Premature Victory Signaling
Bowman’s dissent underscores the potential consequences of prematurely signaling a victory over inflation. Such actions could lead to:
- Relaxation of Consumer and Business Expectations:If the Fed signals that inflation is under control, consumers and businesses may become complacent, leading to increased spending and investment, potentially fueling further inflationary pressures.
- Reduced Incentive for Businesses to Moderate Price Increases:If the Fed signals that inflation is under control, businesses may feel less pressure to moderate their price increases, potentially leading to a resurgence of inflation.
- Market Misinterpretation:A premature signal of victory could lead to misinterpretations in the market, potentially leading to excessive risk-taking and asset bubbles.
Comparison to the Prevailing Sentiment
Bowman’s dissent represents a minority view within the Federal Reserve. While the majority of the FOMC members supported the rate cut, Bowman’s dissenting voice highlights the ongoing debate within the Fed regarding the appropriate course of action to combat inflation.
Implications for the Future
Bowman’s dissent, while seemingly a minor event, could ripple through the financial landscape with significant implications for future Fed decisions, investor confidence, and market volatility. Her dissenting vote signals a potential shift in the Fed’s internal dynamics and could influence the course of future monetary policy.
Potential Impact on Future Fed Decisions, Fed’s Bowman voted against jumbo cut to avoid signaling victory on inflation
Bowman’s dissent highlights a growing concern within the Fed regarding the pace of interest rate hikes and their potential impact on the economy. This dissent could lead to a more cautious approach to future rate decisions, with the Fed potentially opting for smaller increases or even pausing hikes to assess the economic impact of previous actions.
This could also trigger a more robust debate within the Fed regarding the appropriate monetary policy response to inflation and economic growth.
Influence on Investor Confidence and Market Volatility
Bowman’s dissent has already sparked volatility in the financial markets, with investors closely watching for signs of a shift in the Fed’s stance. This uncertainty can lead to increased market volatility, as investors try to decipher the Fed’s future intentions.
A more cautious approach by the Fed could boost investor confidence, as it suggests a less aggressive path towards rate hikes. However, if the Fed remains steadfast in its commitment to fighting inflation, despite the dissent, market volatility could persist.
Potential Scenarios for Future Fed Actions
The following table illustrates potential scenarios for the Fed’s future actions based on various economic indicators:
| Economic Indicator | Scenario 1: Continued Inflation | Scenario 2: Moderating Inflation | Scenario 3: Deflationary Pressures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inflation Rate | > 4% | 3-4% | < 2% |
| Unemployment Rate | < 4% | 4-5% | > 5% |
| GDP Growth | > 2% | 1-2% | < 1% |
| Fed Action | Continued rate hikes | Smaller rate hikes or pause | Rate cuts or quantitative easing |
For example, if inflation remains stubbornly high, the Fed is likely to continue raising interest rates to cool down the economy. However, if inflation starts to moderate, the Fed may opt for smaller rate increases or even pause hikes to assess the economic impact of previous actions.
Conversely, if deflationary pressures emerge, the Fed could cut interest rates or implement quantitative easing to stimulate economic growth.
The Role of Communication: Fed’s Bowman Voted Against Jumbo Cut To Avoid Signaling Victory On Inflation

The Federal Reserve’s communication strategy is a crucial aspect of its monetary policy, impacting market expectations and influencing economic outcomes. Effective communication fosters trust, transparency, and predictability, ultimately contributing to a stable and healthy economy.
Impact of Communication on Market Expectations
The Fed’s communication plays a pivotal role in shaping market expectations. Clear and consistent messaging about its policy intentions helps investors, businesses, and consumers make informed decisions. For example, if the Fed signals a hawkish stance by emphasizing its commitment to fighting inflation, investors might anticipate higher interest rates and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
Conversely, dovish communication, suggesting a willingness to ease monetary policy, could lead to a decline in interest rates and stimulate economic activity.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of Blackbaud EVP sells over $389k in company stock.
Potential Risks and Benefits of Communication Approaches
The Fed’s communication strategy can be approached in various ways, each with its own set of potential risks and benefits. The following table Artikels some of the key communication approaches and their associated implications:
| Communication Approach | Potential Risks | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Explicit Forward Guidance |
|
|
| Data-Dependent Communication |
|
|
| Increased Transparency |
|
|
End of Discussion
Bowman’s dissenting vote serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing challenges facing the Federal Reserve as it seeks to balance economic growth with inflation control. Her cautious approach, while not universally embraced, underscores the need for careful consideration of the potential consequences of premature policy adjustments.
The Fed’s communication strategy will play a critical role in managing market expectations and ensuring economic stability in the face of these uncertainties.
FAQ Corner
What are the potential consequences of signaling victory over inflation prematurely?
Prematurely signaling victory over inflation could lead to a relaxation of monetary policy, which could fuel inflationary pressures and potentially undermine the Fed’s efforts to control inflation.
How might Bowman’s dissent influence investor confidence and market volatility?
Bowman’s dissent could create uncertainty among investors, potentially leading to increased market volatility as they try to assess the implications for future Fed policy.
What is the significance of the Fed’s communication strategy in this context?
The Fed’s communication strategy is crucial for managing market expectations and ensuring economic stability. Clear and consistent communication can help to mitigate uncertainty and foster confidence among investors.
 CentralPoint Latest News
CentralPoint Latest News