Japan CPI inflation hits 10-mth high in August; BOJ meeting approaches – Japan CPI inflation hits a 10-month high in August; BOJ meeting approaches. The news has sent ripples through the Japanese economy, raising questions about the future of monetary policy and the country’s economic trajectory. With energy prices soaring, food costs climbing, and supply chains still grappling with disruptions, inflation has become a significant concern for the Japanese government and the Bank of Japan (BOJ).
The current inflation rate stands in stark contrast to the BOJ’s 2% inflation target, highlighting the challenges the central bank faces in achieving its goals. The BOJ’s upcoming meeting, scheduled for [insert date], will be closely watched as policymakers grapple with the delicate balance between taming inflation and supporting economic growth.
Japan’s Inflationary Surge
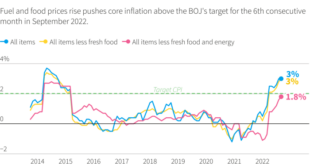
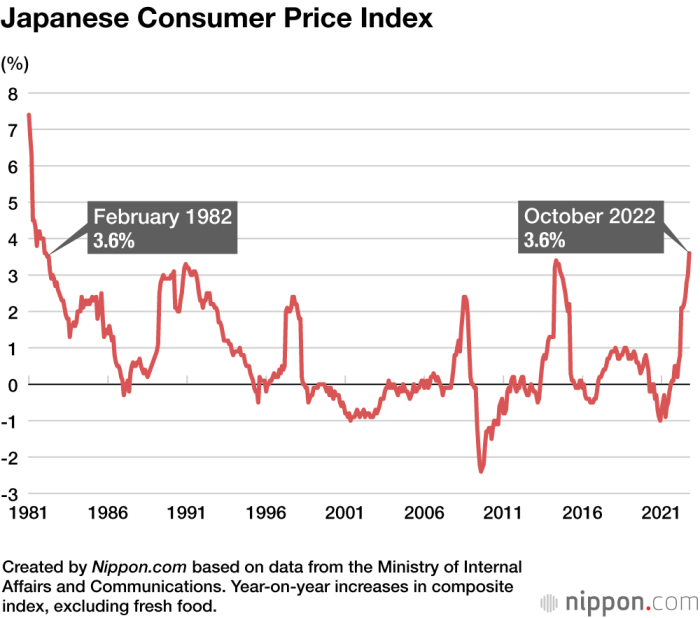
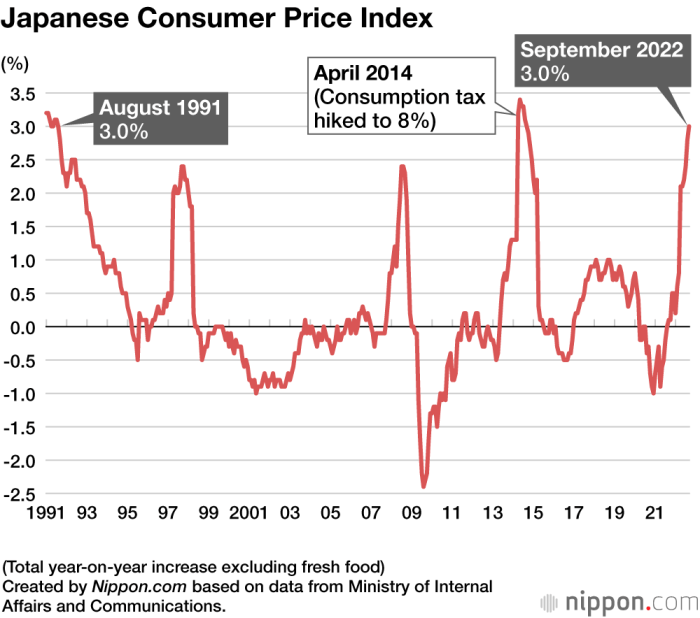
Japan’s economy, known for its stability and deflationary tendencies, is experiencing a significant shift. In August 2023, the country’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation reached a 10-month high, signaling a departure from the prolonged period of low inflation. This surge has caught the attention of economists and policymakers alike, raising questions about the future trajectory of Japan’s economy and the effectiveness of the Bank of Japan’s (BOJ) monetary policies.
Factors Contributing to Inflation
The rise in Japan’s CPI inflation can be attributed to a confluence of factors, primarily driven by global economic trends and domestic supply chain disruptions.
- Energy Prices:The global energy crisis, fueled by the war in Ukraine and increased demand, has significantly impacted Japan’s energy costs. Rising oil and gas prices have pushed up transportation and manufacturing expenses, ultimately feeding into consumer prices.
- Food Costs:Food prices have also risen sharply, driven by factors such as supply chain disruptions, increased demand, and the weak yen. The rising cost of imported food ingredients has impacted the prices of a wide range of consumer goods.
- Supply Chain Disruptions:The ongoing global supply chain disruptions, stemming from the pandemic and geopolitical tensions, have contributed to higher prices for a variety of goods. The shortage of raw materials and components has impacted production costs and led to price increases.
Enhance your insight with the methods and methods of Accel Entertainment CEO sells over $191k in company stock.
Comparison to Historical Trends and the BOJ’s Inflation Target
Japan’s current inflation rate, while significant, remains relatively low compared to historical trends and the BOJ’s inflation target. In the past, Japan experienced periods of deflation, with CPI inflation consistently below 0%. The BOJ’s current inflation target is 2%, aiming to stimulate economic growth and stabilize prices.
The current inflation rate, while a departure from recent trends, is still below the BOJ’s 2% target.
While the recent surge in inflation is a cause for concern, it’s important to note that Japan’s inflation rate remains below the BOJ’s target. The BOJ’s monetary policies, aimed at achieving price stability, will likely play a crucial role in managing the current inflationary pressures.
Impact on the Japanese Economy
Japan’s recent surge in inflation, hitting a 10-month high in August, has significant implications for the country’s economy. The impact of rising prices extends beyond consumer wallets, influencing business decisions and the overall economic landscape.
Consumer Spending
Inflation’s impact on consumer spending is a crucial factor in Japan’s economic outlook. Rising prices erode purchasing power, potentially leading to a decline in consumer spending. This can have a ripple effect throughout the economy, as businesses rely on consumer demand to drive sales and growth.
For example, if food prices rise significantly, consumers might reduce their spending on other goods and services, leading to a slowdown in economic activity.
Business Investment
Inflation can also affect business investment decisions. Rising costs for raw materials, labor, and energy can make it more expensive for businesses to operate and expand. This can discourage investment in new projects, leading to slower economic growth.
Furthermore, uncertainty about future inflation can make businesses hesitant to invest, as they may be unsure about the long-term profitability of their projects.
Exchange Rate
Inflation can influence the exchange rate of the Japanese yen. Higher inflation in Japan compared to other countries can make the yen less attractive to foreign investors, leading to a depreciation of the yen against other major currencies. A weaker yen can make imports more expensive, contributing to further inflation.
However, a weaker yen can also boost exports, as Japanese goods become more competitive in global markets.
Monetary Policy
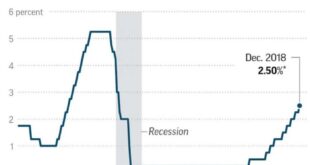
The Bank of Japan (BOJ) closely monitors inflation and its impact on the economy. Inflation above the BOJ’s target range can lead to adjustments in monetary policy. The BOJ might consider raising interest rates to curb inflation and control price increases.
However, the BOJ must balance its inflation concerns with the need to support economic growth. Raising interest rates too aggressively could stifle investment and economic activity.
The Upcoming BOJ Meeting: Japan CPI Inflation Hits 10-mth High In August; BOJ Meeting Approaches
The Bank of Japan (BOJ) is set to hold its next monetary policy meeting in September, where policymakers will carefully assess the latest economic data, particularly the surging inflation, and its impact on the Japanese economy. The BOJ’s decision on whether to maintain its ultra-loose monetary policy or make adjustments to interest rates will have significant implications for the yen’s exchange rate, economic growth, and financial markets.
Key Considerations for the BOJ
The BOJ will consider a number of factors during its upcoming meeting, including:
- Inflation:Japan’s inflation has accelerated in recent months, reaching a 10-month high in August. The BOJ will need to assess the persistence of this inflationary pressure and its potential impact on consumer spending and business confidence. While the current inflation is primarily driven by external factors like rising energy and commodity prices, the BOJ will be looking for signs of a broadening price pressures within the Japanese economy.
- Economic Growth:The Japanese economy is expected to grow at a moderate pace in the coming months. The BOJ will need to balance the need to support economic growth with the need to control inflation.
- Yen’s Exchange Rate:The yen has depreciated sharply against the US dollar in recent months, reaching a 24-year low. This depreciation has contributed to higher import prices, further fueling inflation. The BOJ will need to consider the potential impact of the yen’s weakness on the economy and its ability to control inflation.
Potential Policy Scenarios, Japan CPI inflation hits 10-mth high in August; BOJ meeting approaches
The BOJ has several options for its policy response, including:
- Maintaining the Current Ultra-Loose Monetary Policy:The BOJ could choose to maintain its current policy of negative interest rates and quantitative easing. This approach would continue to provide support for the economy, but it could also exacerbate the yen’s depreciation and make it more difficult to control inflation.
- Adjusting Interest Rates:The BOJ could raise interest rates, either gradually or more aggressively. This would help to curb inflation but could also slow economic growth and further weaken the yen. The BOJ will need to carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks of raising interest rates.
- A Combination of Policies:The BOJ could also choose to implement a combination of policies, such as a small interest rate hike combined with continued quantitative easing. This approach would provide a more nuanced response to the current economic situation.
Consequences of Different Policy Decisions
The BOJ’s policy decisions will have significant consequences for the Japanese economy and financial markets.
- Maintaining the current ultra-loose monetary policy:This could lead to further depreciation of the yen, making it more expensive for Japanese businesses and consumers to import goods and services. This could also lead to higher inflation and a potential loss of confidence in the Japanese economy.
- Adjusting interest rates:This could help to curb inflation but could also slow economic growth and further weaken the yen. A sharp increase in interest rates could also lead to a rise in borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, potentially slowing investment and spending.
- A combination of policies:This could be a more balanced approach, providing some support for the economy while also helping to control inflation. However, the effectiveness of this approach will depend on the specific policies implemented and the timing of their implementation.
Global Economic Context
Japan’s recent inflationary surge and the Bank of Japan’s (BOJ) policy decisions have global implications, potentially influencing the trajectory of the global economy. This section explores how Japan’s economic developments might impact global economic conditions, comparing the current situation with inflation trends in other major economies, and analyzing the potential spillover effects of Japan’s monetary policy on global financial markets.
Impact on Global Economic Conditions
Japan’s inflationary pressures, while still relatively moderate compared to some other developed economies, could contribute to global inflation by raising input costs for businesses operating globally. Japan is a major exporter of manufactured goods, including automobiles, electronics, and machinery. If the yen weakens significantly due to the BOJ’s accommodative monetary policy, Japanese exports could become more competitive, potentially leading to increased demand and higher prices in global markets.
This could exacerbate existing inflationary pressures in other countries, particularly those reliant on Japanese imports.
Closure
As the BOJ prepares to make its decision, the eyes of the world are on Japan. The outcome of this meeting will not only shape the future of the Japanese economy but could also have far-reaching implications for global markets.
Whether the BOJ chooses to maintain its ultra-loose monetary policy or adjust interest rates, the decision will have significant consequences for the Japanese yen, consumer spending, and business investment. The world waits with bated breath to see how Japan navigates this complex economic landscape.
FAQ Corner
What are the key factors driving inflation in Japan?
Rising energy prices, increased food costs, and ongoing supply chain disruptions are the primary contributors to Japan’s recent inflationary surge.
How might inflation affect the Japanese yen?
Rising inflation could weaken the Japanese yen as investors seek higher returns in other currencies. However, the BOJ’s policy response could also influence the yen’s exchange rate.
What are the potential consequences of the BOJ’s policy decisions?
The BOJ’s decision could impact the Japanese economy’s growth, inflation, and the yen’s value. A tightening of monetary policy could slow economic growth but potentially curb inflation. Conversely, maintaining a loose monetary policy could fuel inflation but support economic expansion.
 CentralPoint Latest News
CentralPoint Latest News